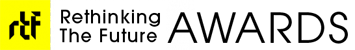Lines found in nature are directly transferred onto garments. Korean traditional houses are called Hanok (Hangul:한옥) .Sites of residence are traditionally selected using traditional geomancy. A house should be built against a hill and face south to receive as much sunlight as possible. This orientation is still preferred in modern Korea. Geomancy also influences the shape of the building, the direction it faces and the material it is built of.
Participant Name: Tsogtbileg Batsaikhan
University: Sahmyook university
Country: South Korea

Traditional Korean houses can be structured into an inner wing (안채, anchae) and an outer wing (사랑채, sarangchae). The individual layout largely depends on the region and the wealth of the family. Where as aristocrats used the outer wing for receptions, poorer people kept cattle in the sarangchae. The wealthier a family, the larger the house. A kan is the distance between two pillars used in traditional houses. The inner wing normally consisted of a living room, a kitchen and a wooden-floored central hall. More rooms may be attached to this. Poorer farmers would not have any outer wing. Floor heating (온돌, ondol) has been used in Korea since prehistoric times.
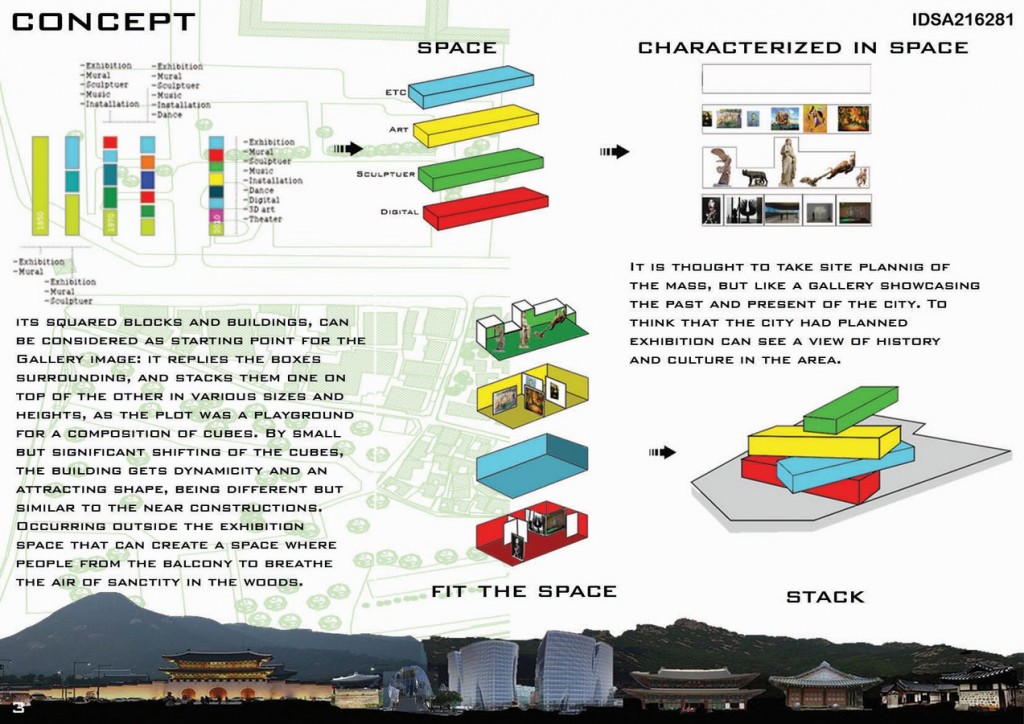
The main building materials are wood, clay, tile, stone, and thatch. Because wood and clay were the most common materials used in the past not many old buildings have survived into present times. Life sucks up there. For you, for me, for trees, and just about everything else except peregrine falcons. It’s hot, cold, windy, the rain lashes at you, and the snow and sleet pelt you at high velocity.
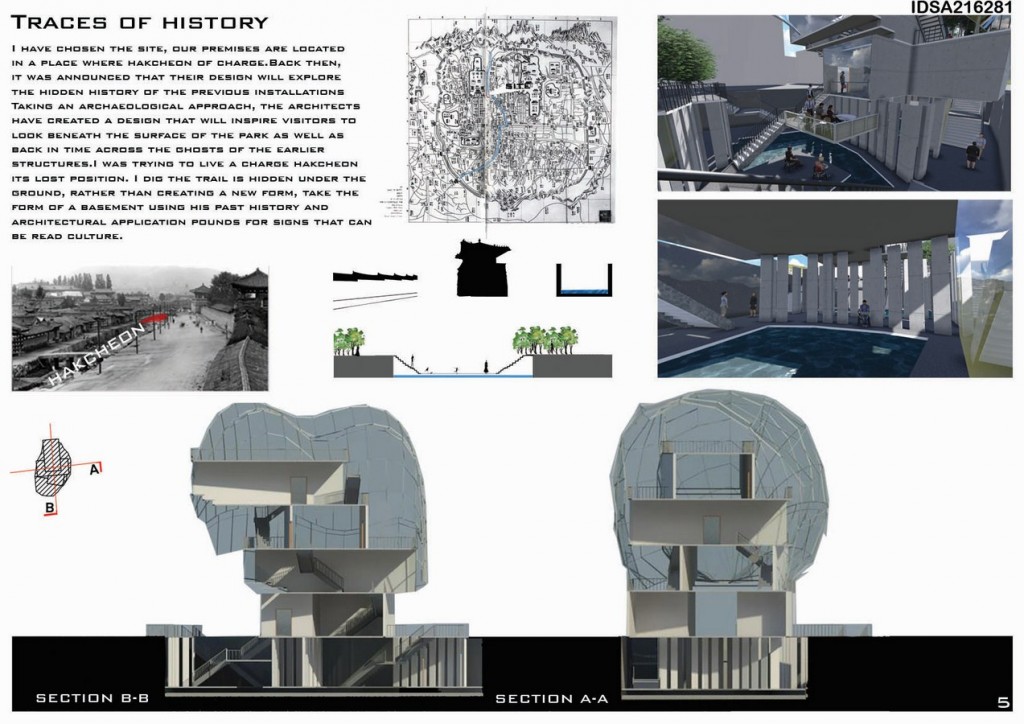
Life for city trees is hard enough on the ground. City trees have enough trouble finding enough space for their roots at ground level in sidewalk planters, and even if they survive, they rarely grow much bigger than they were when they were planted.
Prev Post
Qajar Music Museum | Javad Eiraji
2 Mins Read