Informal Surgery is an urban design proposal, in which a series of architectural objects are surgically added after a critical examination of Kumbharwada – the potters’ settlement in Dharavi which is the largest informal settlement in India.
Global Design & Architecture Design Awards 2021
First Award | Category: New Design Talent – Urban Design
Project Name: Informal Surgery
Project Category: New Design Talent | Urban Design (Concept)
Studio Name: Dasthapati
Design Team: Deepankar Sharma with Graham Crist
Area: 5.2 Hectares
Year: 2021
Location: Dharavi, Mumbai, India

The purpose of this is to enhance the environment for the residents of Kumbharwada, to thrive and prosper. The added objects are Sanitation Facilities reminiscing “Baoli” – Indian Stepwells, Residential Units recalling “Haveli” – Traditional Mansion, Smoke Infrastructures following the traditional construction methods and Public Spaces inspired by “Baithak” – A Communal Space. An eager endeavour is made to not merely address the issues at the site but to formulate an environment that the residents rejoice and relish. The operation is conducted in four blocks of the settlement and proposes “a base model” that can be expanded to all the blocks in the site.
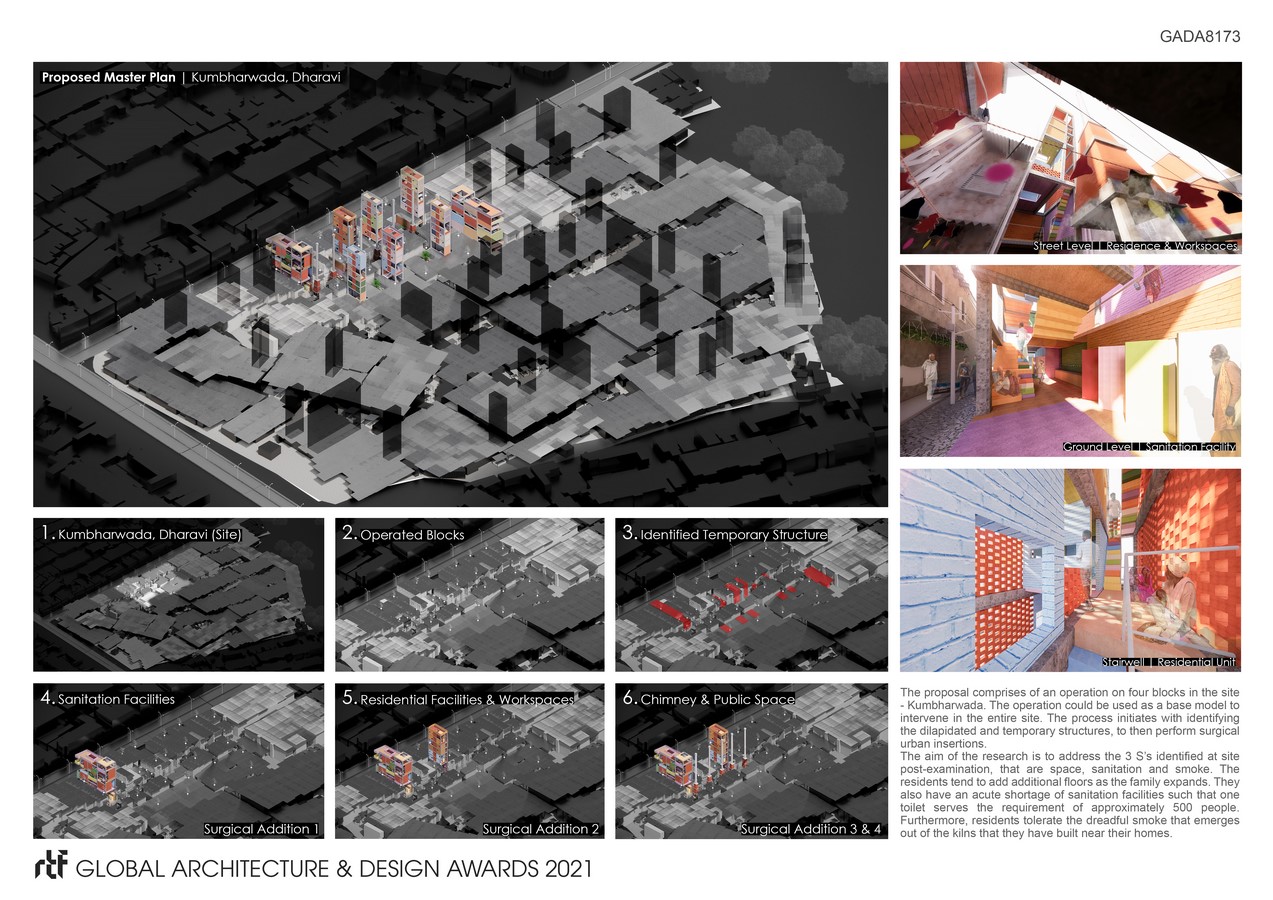
The proposed redevelopment plan is an intermediate alternative between the existing informal settlement and the state’s proposal for total clearance of the informal settlement. Similar strategies can be adopted in all the settlements in Dharavi to rehabilitate the environment for the residents who are in dire need of an upliftment through an upgraded neighbourhood.

Rules for Urban Insertions
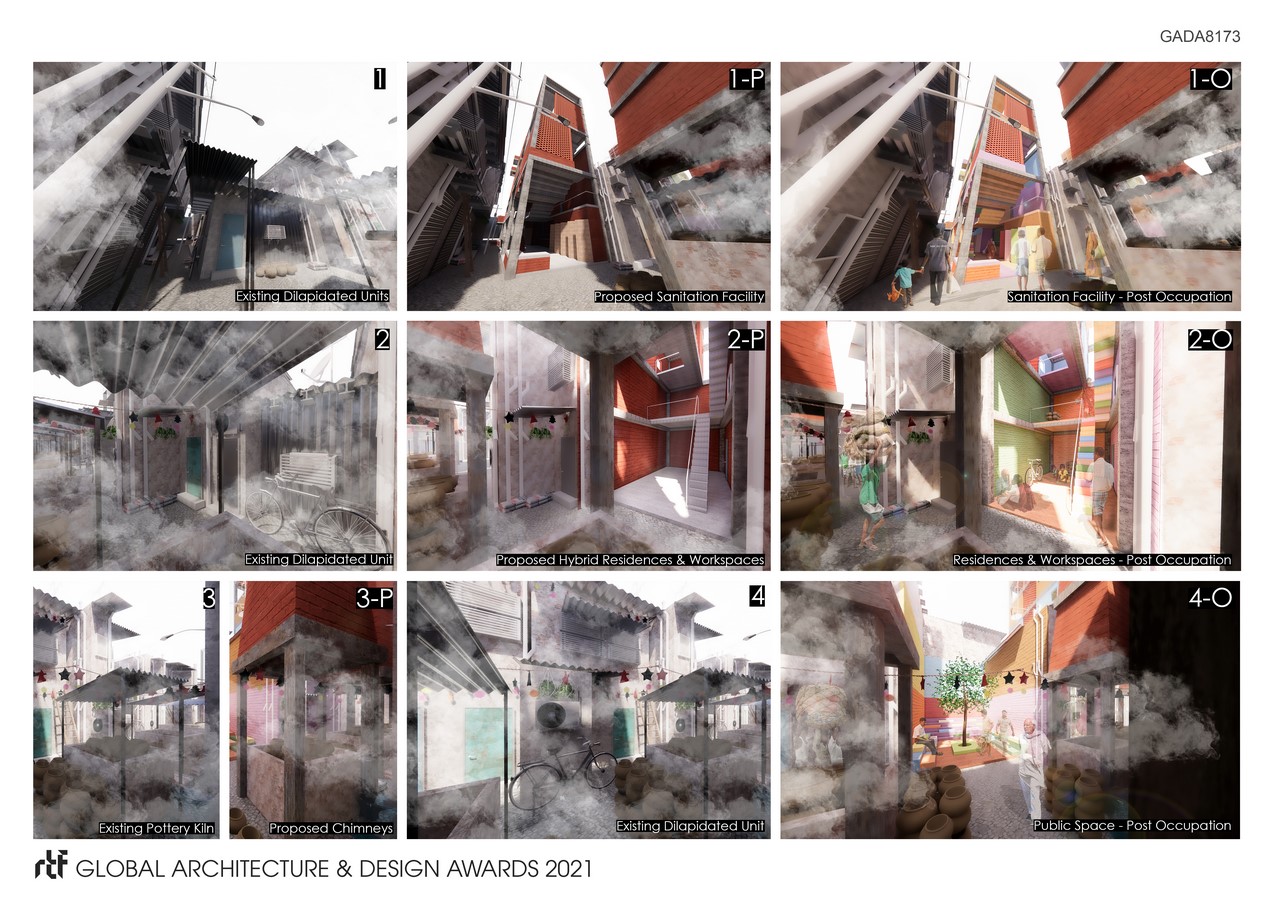
Keeping the current density, this research endeavours to make rules to surgically intervene at the site. Firstly, maintaining the individual plot boundaries. Secondly, retaining the block dimension. And thirdly, conserving the streetscape. The research operates on four blocks in the site. The process initiates with identifying the dilapidated and temporary structures, to then perform surgical urban insertions.

Sanitation Facility
An architectural object is surgically added to provide sanitation facility in the block for the residents, by replacing two identified units. While, the framework of the object is designed to facilitate sanitation, the spaces can be customised by the residents through their own colours, textures and patterns. The facility reminisces traditional Indian stepwells as a classical precedent of a bathing space with strong communal characteristics.
Residential Units
The second surgical insertion is an object that facilitates 3 residential units and working spaces. An operation on the existing dilapidated unit is conducted to inject the residential facilities. The inhabitants are envisaged to bring the object to life through their distinguished colours, textures and spaces. The proposed residential unit recalls traditional Indian havelis with embedded courtyards. This is done to translate its qualities at site. Individual units are 6 meters high and follow the examined incremental principles at the site. The aim for the proposed stairwell is to
expand the transitional qualities and incorporate a sense of community observed in traditional Havelis.
Smoke Infrastructure
The third surgical insertion is a chimney to all the kilns to reduce the amount of smoke experienced by the residents. The incorporation of the chimney follows the traditional construction methods in India.
Public Space
This surgical operation is to plant a communal space in the place of an obsolete residential unit. This intervention reminisces “Baithak” – a community gathering space where people share and discuss ideas, issues, learnings and teachings.